Clean Air Europe first developed its Photohydroionization® (PHI-CELL®) technology over 20 years ago and since then more than four million units have been installed worldwide. Over the years the PHI-Cell evolved into the REME-HALO® and now the widely popular HALO-LED™.
RGF® has licensed its technology to many Fortune 500 companies for use in health care, food processing, military, government, marine, hospitality, residential and commercial applications. In addition, RGF®’s PHI-Cell technology has been specified in the Norovirus and MRSA protection plan of America’s largest restaurant chains, hotel chains, theme parks, cruise lines and public school.
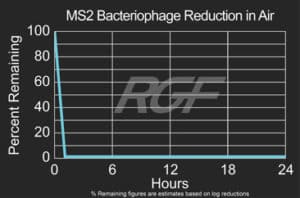
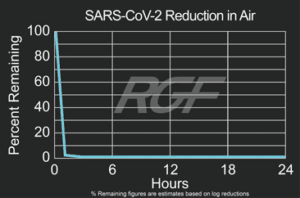
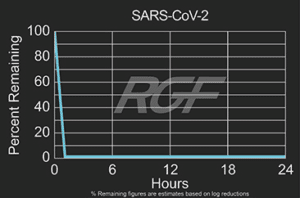
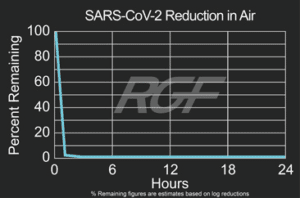
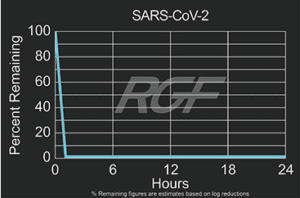
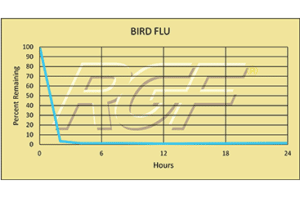
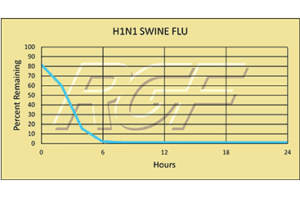
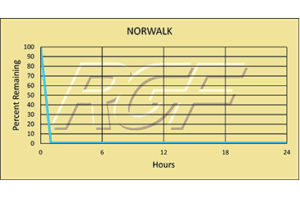
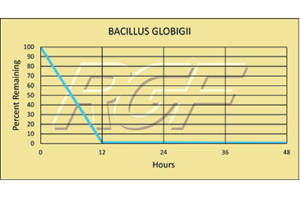
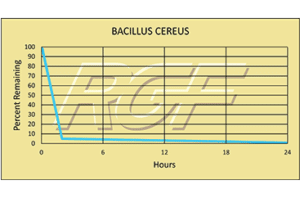
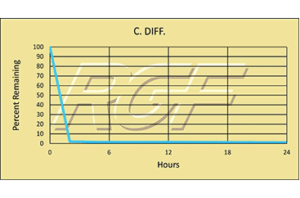
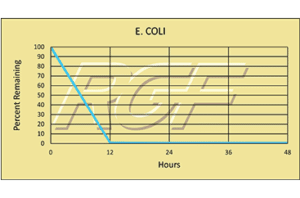
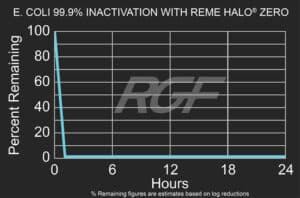
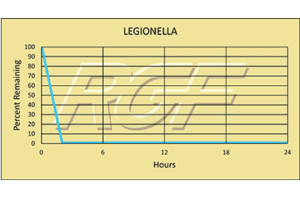
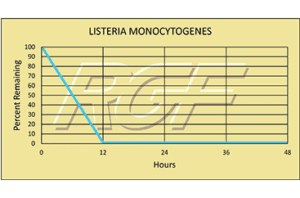
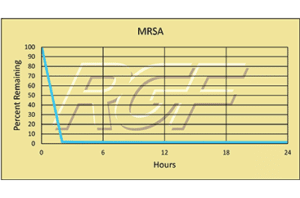
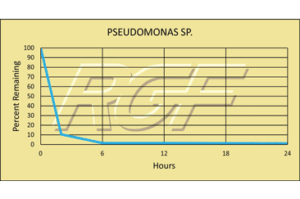
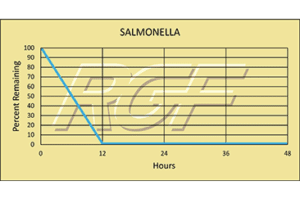
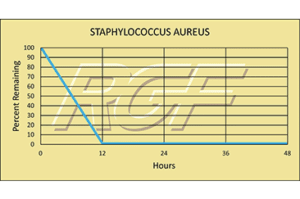
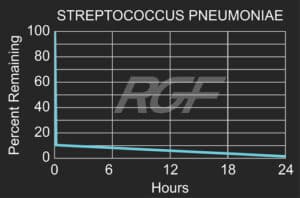
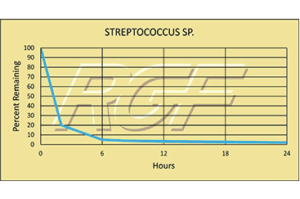
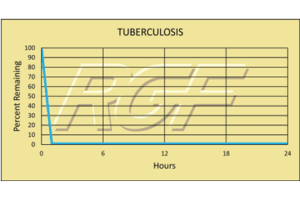
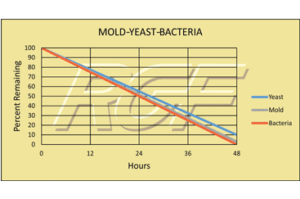
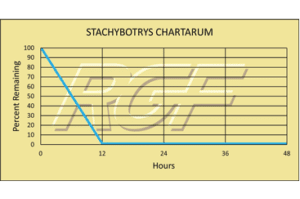
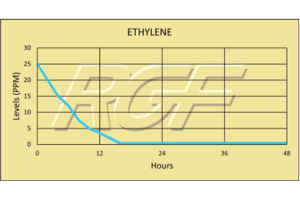
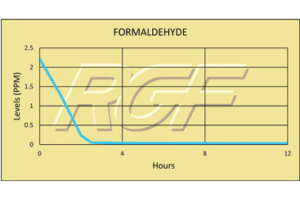
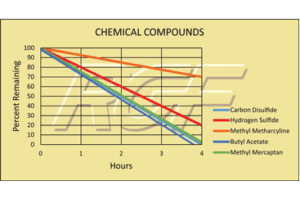
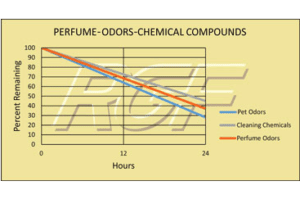
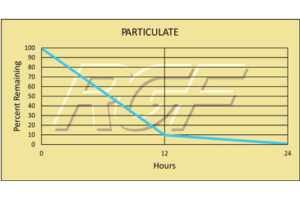
Below you will find a summary of some of the testing and studies performed by third party independent labs and universities. While the research is compelling, RGF® PHI-Cell products are not medical devices and no medical claims are made.